ManyLaws High-Level Architecture
ManyLaws will implement an ICT architecture, supporting the integration of the pool of identified services while keeping the structure flexible allowing the inclusion of further services and data sources. A layered approach supporting the data flow, from source data to visualised outputs is to handle the large volumes of data. The following figure presents the high-level IT architecture along with the indicative components to be incorporated.
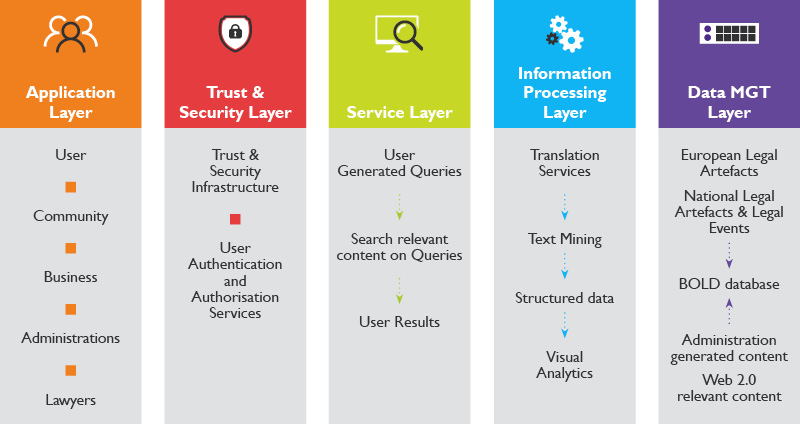
Application Layer
The application layer features the following two modes of operation:
Community Mode: The Community Mode will incorporate a number of social features that can promote ManyLaws user engagement aspects, such as analytics provision, integration of news feed and social media connectors. The social infrastructure of EU-Community project will be reused to support the community interactions and also embed the assembly of EU stakeholders interactions.
User Mode: In order to gain insight into the processed results a user-centred approach will be followed to design and develop a web interface that will provide to the ManyLaws users interactive access to the Visual Analytics services. In the User Mode, meaningful and attractive visualizations of search outcomes and their semantics will be displayed in order to allow not only experts but also ordinary people to explore and interact with versatile legal information in an intuitive manner. The whole layer will follow a responsive web design in order for users to have access on the results through a mobile interface, apart from the web one.
Trust and Security Layer
Trust and Security Infrastructure: The trust and security infrastructure will provide the trust management and the efficient security provisioning (like crypto-primitives, crypto-protocols, public key infrastructure / PKI integration, digital rights management / DRM systems coverage, dependability assurance, risk prediction algorithms) needed for every component of the ManyLaws platform. ManyLaws will build and extend the openlaws project security architecture.
User MGT Authentication and Authorization Services: User MGT Authentication and Authorization Services will ensure that users can rely on the ManyLaws platform and that the platform is protected against unauthorized access and attacks. The rights for the users in the Community Mode, the User Mode, the Business Mode and Administration Mode for the different users will be cleared and managed in the User Management Authentication and Authorization Services. After registration users will be able to log-in to the service and adjust their personal settings.
Service Layer
User Generated Queries: The ManyLaws infrastructure will store search queries made by users for analysis and optimization purposes. The terms and structure that make up the user query will be fed into the Semantic search Engine to enhance the relevance of the results based on inferred concepts and semantic annotations. In addition, due to the resource intensiveness of semantic querying, this component will apply optimization methods to prioritise queries, cache results results, or even explore innovative methods for scaling such as Linked Data Fragments7.
Search relevant content based on queries: The ManyLaws Search Engine will be used for searching through the system’s triple store using a scalable Solr-based semantic search engine. ManyLaws search engine will be taking into account semantic relations between search terms and stored entities (e.g. synonyms). Best practices such as faceted search will also be used to present the user with more search options, relevant to the search terms by semantic association.
Search results: This component will be responsible for retrieving and presenting to the user the search results in an efficient and user-friendly manner.
Information Processing Layer
Data Preparation and Translation Services: This is the stage where data is acquired and prepared for the text mining tools to follow. The stages includes data reading and initial cleansing, anonymization if needed, semantic annotation (so that to be indexed at the European Open Data Portal), and formulation for processing. Due to the diversified origin of the texts to be acquired, a large amount of effort and computational power will have to be devoted to Optical Character Recognition and translation in English, if in a different member state official language. Translation will be based on EUROVOC and automated translation services, both for the complete texts but also for the various indexes and n-grams to be create at the processing stage.
Text Mining: Various algorithms will be applied in different processing tasks, relying on a super-computing infrastructure, in order to produce service – oriented intermediate results:
- Creation of reverse indexing, occurrence and frequency tables for millions of words
- Creation of various n-grams for the identification of important terms or phrases
- Semantic comparison of different law sets (e.g. EU Directive against national legal framework) performing full word-level, document-to-document comparison for billions of pages – needing the power of thousands processors
- Interrelation of all the original and translated terms and texts
- Term extraction analysis of news, social media, blogs and other content
Structured Data: This component represents the information collected from the various sources harvested by the Data Sources Layer, and adhering to a common model and format, that can then be used more effectively by the Visual Analytics Service. The data stored here will include any harvested and derived information that is necessary to realise the project’s use cases.
Visual Analytics Service: The Visual Analytics Service provides the ability to access the entire data transformation pipeline from raw or semantic data to interactive visual representations. The main goal is to enable user-centred and comprehensible solutions for getting insights and knowledge about the entire domain. Visual Analytics as a service further enables solving the variety of knowledge related questions in the domain of law. The service characteristics enable to exploit the technology to other domains. The variety of visualizations and transformation technologies will be adaptable to user’s requirements and support her in the knowledge acquisition process.
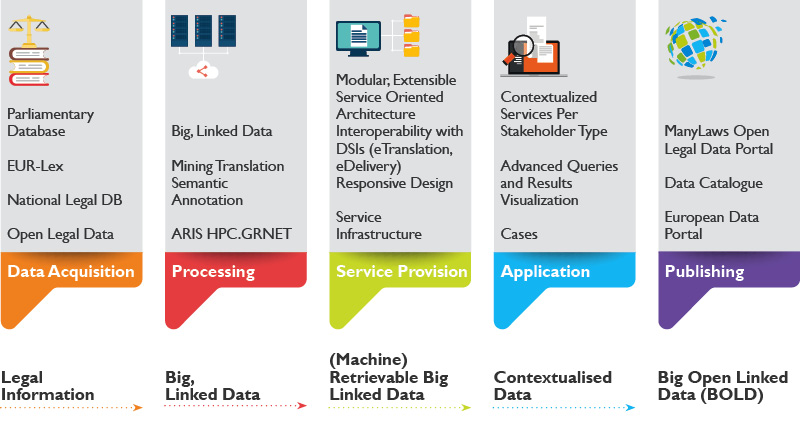
Data Sources Layer
Data Repository: The data sources to be accessed primarily through web services communication where available.
Access to the portal will become available on 31 March 2020.


